
Why QVAR
Small airways make up more than 98% of the lung.1
The small airways are involved in all stages of asthma including night-time asthma, exercise-induced asthma, allergy-induced asthma, difficult-to-control asthma and those at risk of repeated asthma exacerbations.1,2
In children, uncontrolled or untreated small airway inflammation is related to permanent damage to the lung and irreversible loss of lung function.2,3
QVAR is designed to treat inflammation of the lung in both the large and small airways.
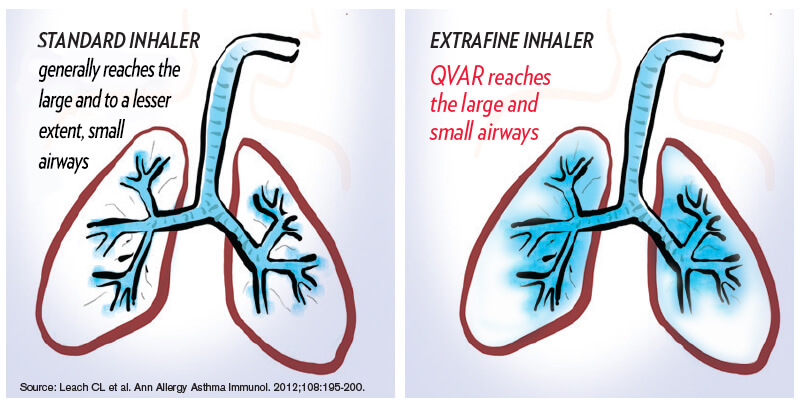
The lungs are made up of large and small airways. Asthma is a disease of chronic lung inflammation that affects both the large and small airways.4,6
If left untreated, this inflammation can cause damage to the airways in the lungs and can be associated with asthma attacks and difficulty breathing.5
QVAR extrafine preventer inhaler contains very small particles of asthma medicine, small enough to reach and treat inflammation in both the large and also deep into the small airways of the lungs.
QVAR is a twice-daily extra fine asthma preventer medicine. The QVAR asthma inhaler is approved to help manage asthma and is an asthma preventer inhaler in New Zealand that can treat inflammation in the small airways.
QVAR is a daily extrafine inhaler that works over time to reduce inflammation on your air passages. This helps to improve your condition and to prevent asthma attacks from occurring.
Maintaining long-term asthma control
QVAR is an extrafine asthma preventer medicine that should be taken every day to help keep asthma symptoms under control – even if you are feeling better and not experiencing symptoms.
Forgetting to take asthma preventer medicine like QVAR – or stopping because your symptoms aren’t present – may increase the risk of asthma attacks.
It is also important to know what to do in an emergency. Get an Asthma Action Plan today from your healthcare provider.
References: 1. Carr TF, Altisheh R, Zitt M. Small airways disease and severe asthma. World Allergy Organ J. 2017;10(1):20. Published 2017 Jun 21. doi:10.1186/s40413-017-0153-4 2. Bjermer L. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2014;20:23-30. 3. Hirota N & Martin JG. Chest 2013 Sep;144(3):1026-32. 4. https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/ajrccm.159.supplement_2.mfa-1#readcube-epdf.
5. https://www.webmd.com/asthma/features/preventing-permanent-damage#1 6. Leach, et al. Characterization of respiratory deposition of fluticasone-salmeterol hydrofluoroalkane-134a ad hydrofluoroalkane-134a beclomethasone in asthmatic patients. An Allergy Asthma Immunol . 2012;108 (3):195-200.

